Preventive and avoidance-based treatments to combat or resolve temporomandibular disorders are essential to relieving chronic pain. These procedures can be administered based on the circumstances or levels of pain. Self-limiting disease or non-progressive pain is an...
Diagnostic Tests for Temporomandibular Disorders
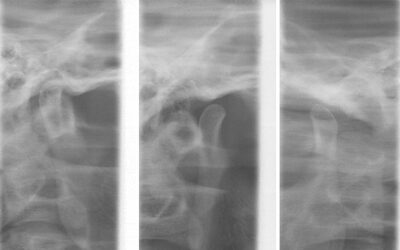
In this article we'll explore three primary tests to help diagnose temporomandibular disorders: Imaging tests Physical medicine tests Serologic tests 1. Imaging Tests A. Panoramic Radiographs A panoramic radiograph is utilized primarily to have a general vision of the...
Arthritic Temporomandibular Joint Disorders
Arthralgia or Capsulitis Arthralgia/Capsulitis is defined as a painful joint (even without any osseous changes) with increased tenderness to palpation pressure. The clinical history and examination evidence needed for this diagnosis includes: A unilateral or bilateral...
Internal Derangements of the Temporomandibular Joint
Internal Derangement is not a diagnosis but a category of conditions and it simply means abnormal function of the intra-articular structures. It is a non-specific term applied as a descriptive subdivision term for the group of non-arthritic TM joint disorders (e.g.,...
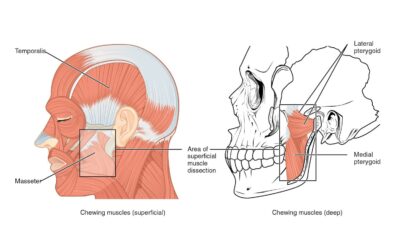
How to Diagnose Masticatory Muscle Disorders
Localized Myalgia Localized myalgia is a term used to describe a dull aching continuous which the patient localizes to muscles in the masticatory system (usually the masseter and temporalis) or cervical muscles (SCM and trapezius). If the myalgia is in...
How to Insert and Adjust Occlusal Stabilization Appliances
There are four primary elements that form the theoretical basis for an occlusal stabilization appliance: It protects teeth from wear It stabilizes an unstable bite It makes the patient more aware of any oral habit It allows you to reduce loading on a specific...
Oral Laser Ablation Surgery: Step-by-Step Guide for Dentists
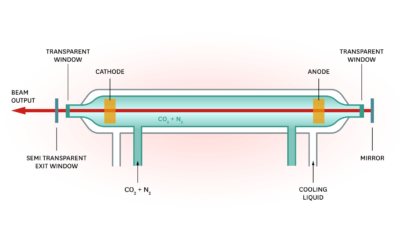
What is a laser? Lasers are an intense, high energy, coherent (travels in a constant phase in time and space), monochromatic (a single wavelength particular to the medium), and collimated (travels in the same direction) electromagnetic radiation that is produced by a...
Step-by-Step Instructions for Performing Oral Cryotherapy
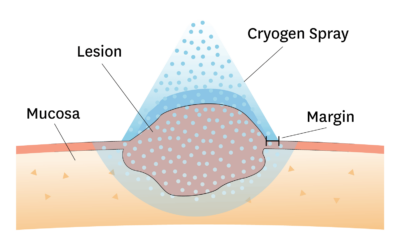
Oral Cryotherapy Oral cryotherapy is a very safe, easy to perform, and relatively inexpensive treatment for various selected oral lesions. You should never perform cryotherapy unless you know the diagnosis of the lesion you to freeze. HPV is associated with...
How to Perform a Jaw Bone Biopsy
What is a jaw bone biopsy? When you use the term “bone biopsy,” this could mean you are taking a piece of bone or you are taking tissue that resides inside a bone. There are two approaches for a bone biopsy. A closed/needle bone biopsy involves inserting a...
Minor Salivary Gland Biopsy for Diagnosing Sjogren’s Syndrome
Minor Salivary Gland (MSG) Biopsy Minor salivary gland (MSG) biopsy of the lower lip mucosa is used to confirm the diagnosis of Sjogren’s syndrome. Sjogren’s is a chronic autoimmune disorder involving the destruction of glandular tissue. Sjögren's syndrome can cause...
How to Conduct an Oral Cavity Punch Biopsy
What is a punch biopsy? An oral cavity punch biopsy is considered the primary technique to obtain diagnostic, full thickness skin specimens. It is performed using a circular blade or trephine attached to a pencil-like handle. The instrument is rotated down through...
How to Perform an Oral Biopsy
A biopsy is defined as the sampling or removal of tissues or liquids from the body for examination, in order to determine the existence or cause of a disease. A biopsy is strongly recommended for most of the lesions that persist for more than two weeks which...
Trigger Point Mapping: Theory & Step-by-Step Technique
What is a trigger point? A trigger point is due to sensitized sensory nerves within a taut band of a muscle that when squeezed generates local and referred pain. The cause of a taut band is a hyperactive motor nerve branch, which generates sustained contraction in the...
How to Administer a Gingival Cold Test
This test is utilized when you have a focal, intraoral, probable neuropathic pain disorder involving a branch of the trigeminal nerve with palpable gingival allodynia/hyperalgesia and no obvious, local dental pathology exists such as tooth fractures, periapical...
How to Perform a TMJ Injection
TMJ injections are performed with corticosteroid and anesthetic to produce a two-fold effect: one reduce inflammation with the corticosteroid (triamcinolone acetonide) and two produce anesthesia or pain relief using lidocaine 2% without epinephrine. ...
How to Measure Orofacial Pain With a Muscle Tenderness Exam
In this article, we review ways to assess muscle tenderness and pain. Common abnormalities of the masticatory muscle include injection induced myositis, myofascial taut band, trigger point, hypertrophy, spasms, etc. Note: Prior to each procedure, introduce...
How to Conduct a Cranial Nerve Examination
The following equipment is required for a Cranial Nerve Examination: Cotton ball Safety pin Pen torch (source of light) Tongue blade Tuning fork (512 Hz) 1.) Olfactory Nerve (I) The olfactory is a sensory nerve, and damage in the nasal epithelium or the basal...
Closed Lock Mobilization: TMJ Exercises & Stretches
In this article, we'll provice step-by-step TMJ exercises and treatments for Dentists and self-mobilization stretches for patients. The main reason why a jaw locks closed is due to a derangement of the TM joint (disk displacement without reduction or DDNR). It is...
How to Perform an Occlusal Analysis
Occlusion, simply defined, is how teeth meet when the lower and upper jaw come together. Proper occlusion is necessary for eating, aesthetics, and disease prevention. However, many factors can cause malocclusion including trauma and genetics. Before we...
TMJ Assessment: Jaw Range of Motion, Noise, and Tenderness
X-ray image showing articular fossa and condyle.For TMJ mobilization procedures read: Closed Lock Mobilization: TMJ Exercises & Stretches. Jaw Range of Motion Assessment Prior to the procedure, introduce yourself to the patient, explain the purpose of the...
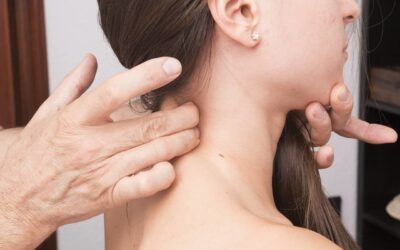
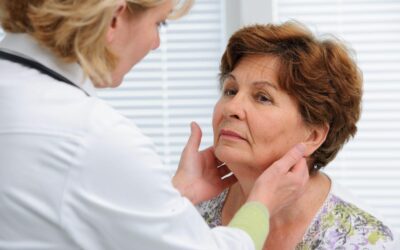
How to Perform a Lymph Node Examination
Lymph Node Examination A lymph node evaluation should be included in all new patients as part of the oral cancer triage. Below is a video showing the proper technique and a written explanation of what is expected from dentists when performing a lymph node and...
Proposed Mechanism and Treatment of Palatal Myoclonus
Myoclonus is a frequently observed hyperkinetic movement disorder, which is often classified according to its anatomical origin. [1] Palatal myoclonus is characterized by involuntary palatal contractions, causing clicking tinnitus due to the action of soft palate...
Mechanism and Treatment of Orofacial Motor Tics
Rather than a voluntary movement, a tic is a movement which relieves a voluntary urge, and this is the key characteristic which differentiates a tic from another movement disorder. Motor tics of the orofacial area include tongue protrusion, facial grimacing, blinking,...
Teledentistry – Frequently Asked Questions
These FAQs were collected from a recent webinar on Telehealth & COVID-19 presented by the Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry with Dr. Glenn Clark, Professor Linda Brookman, Dr. Kamal Aleryani, and Dr. Steven Richeimer. What is Teledentistry in 2020? “Teledentistry”...